| INTRODUCTION:
Bhutan ; Dzongkha Dru u, IPA: officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia at the eastern end of the Himalayas. It is bordered to the north by China and to the south, east and west by India. To the west, it is separated from Nepal by the Indian state of Sikkim, while farther south it is separated from Bangladesh by the Indian states of Assam and West Bengal. Bhutan’s capital and largest city is Thimphu. Bhutan existed as a patchwork of minor warring fiefs until the early 17th century. At that time the lama and military leader Ngawang Namgyal, the first Zhabdrung Rinpoche, who was fleeing religious persecution in Tibet, unified the area and cultivated a distinct Bhutanese identity. In the early 20th century, Bhutan came into contact with the British Empire and retained strong bilateral relations with India upon its independence. In 2006, based on a global survey, Business Week rated Bhutan the happiest country in Asia and the eighth-happiest in the world. The country’s landscape ranges from subtropical plains in the south to the sub-alpine Himalayan heights in the north, where some peaks exceed 7,000 metres (23,000 ft). Its total area was reported as approximately 46,500 km(18,000 sq mi) in 1997 and 38,394 km (14,824 sq mi) in 2002. Bhutan’s state religion is Vajrayana Buddhism and the population, as of 2015 estimated as 770 thousand people, is predominantly Buddhist. Hinduism is the second-largest religion. |
 |
| GEOGRAPHY
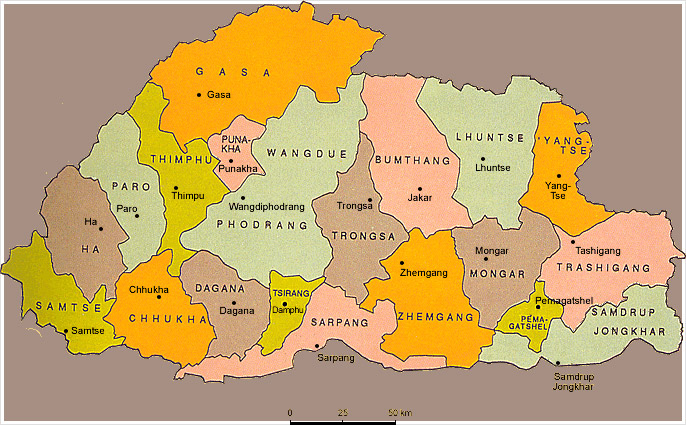
Bhutan is located on the southern slopes of the eastern Himalayas, landlocked between the Tibet Autonomous Region to the north and the Indian states of Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh to the west and south. It lies between latitudes 26°N and 29°N, and longitudes 88°E and 93°E. The land consists mostly of steep and high mountains crisscrossed by a network of swift rivers, which form deep valleys before draining into the Indian plains. Elevation rises from 200 m (660 ft) in the southern foothills to more than 7,000 m (23,000 ft). This great geographical diversity combined with equally diverse climate conditions contributes to Bhutan’s outstanding range of biodiversity and ecosystems. The northern region of Bhutan consists of an arc of Eastern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows reaching up to glaciated mountain peaks with an extremely cold climate at the highest elevations. Most peaks in the north are over 7,000 m (23,000 ft) above sea level; the highest point in Bhutan is Gangkhar Puensum at 7,570 metres (24,840 ft), which has the distinction of being the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. The lowest point, at 98 m (322 ft), is in the valley of Drangme Chhu, where the river crosses the border with India. Watered by snow-fed rivers, alpine valleys in this region provide pasture for livestock, tended by a sparse population of migratory shepherds. The Black Mountains in the central region of Bhutan form a watershed between two major river systems: the Mo Chhu and the Drangme Chhu. Peaks in the Black Mountains range between 1,500 and 4,925 m (4,921 and 16,158 ft) above sea level, and fast-flowing rivers have carved out deep gorges in the lower mountain areas. The forests of the central Bhutan mountains consist of Eastern Himalayan subalpine conifer forests in higher elevations and Eastern Himalayan broadleaf forests in lower elevations. Woodlands of the central region provide most of Bhutan’s forest production. The Torsa, Raidak, Sankosh, and Manas are the main rivers of Bhutan, flowing through this region. Most of the population lives in the central highlands. In the south, the Shiwalik Hills are covered with dense Himalayan subtropical broadleaf forests, alluvial lowland river valleys, and mountains up to around 1,500 m (4,900 ft) above sea level. The foothills descend into the subtropical Duars Plain. Most of the Duars is located in India, although a 10 to 15 km (6.2 to 9.3 mi) wide strip extends into Bhutan. The Bhutan Duars is divided into two parts: the northern and the southern Duars. The northern Duars, which abut the Himalayan foothills, have rugged, sloping terrain and dry, porous soil with dense vegetation and abundant wildlife. The southern Duars has moderately fertile soil, heavy savannah grass, dense, mixed jungle, and freshwater springs. Mountain rivers, fed by either the melting snow or the monsoon rains, empty into the Brahmaputra River in India. Data released by the Ministry of Agriculture showed that the country had a forest cover of 64% as of October 2005. |
 |
| CLIMATE:
The climate in Bhutan varies with elevation, from subtropical in the south to temperate in the highlands and polar-type climate, with year-round snow in the north. Bhutan experiences five distinct seasons: summer, monsoon, autumn, winter and spring. Western Bhutan has the heavier monsoon rains; southern Bhutan has hot humid summers and cool winters; central and eastern Bhutan is temperate and drier than the west with warm summers and cool winters. |
|
| PEOPLE OF BHUTAN
Approximately two-thirds to three-quarters of the population practice Drukpa Kagyupa or Ningmapa Buddhism, both of which are disciplines of Mahayana Buddhism. Approximately one-quarter of the population is ethnic Nepalese and practice Hinduism. They live mainly in the south and follow the Shaivite, Vaishnavite, Shakta, Ghanapathi, Puranic, and Vedic schools. Christians both Roman Catholic and Protestant and nonreligious groups comprised less than 1 percent of the population. Bön, the country’s animist and shamanistic belief system, revolves around the worship of nature and predates Buddhism. Very few citizens adhere exclusively to this religious group. |
|
| RELIGION OF BHUTAN:
It is estimated that between two-thirds and three-quarters of the Bhutanese population follow Vajrayana Buddhism, which is also the state religion. About one-quarter to one-third are followers of Hinduism. Other religions account for less than 1% of the population. The current legal framework, in principle guarantees freedom of religion; proselytism, however, is forbidden by a royal government decision and by judicial interpretation of the Constitution. Buddhism was introduced to Bhutan in the 7th century AD. Tibetan king Songtsän Gampo (reigned 627–649), a convert to Buddhism, ordered the construction of two Buddhist temples, at Bumthang in central Bhutan and at Kyichu Lhakhang (near Paro) in the Paro Valley. |
|
